Note: We use fill-in-the-blank questions to approximate the style of paper 2 questions while allowing for automatic grading. But you should test yourself by trying to write the entire answer from memory.
Quiz Summary
0 of 2 Questions completed
Questions:
Information
You have already completed the quiz before. Hence you can not start it again.
Quiz is loading…
You must sign in or sign up to start the quiz.
You must first complete the following:
Results
Results
Your time:
Time has elapsed
You have reached 0 of 0 point(s), (0)
Earned Point(s): 0 of 0, (0)
0 Essay(s) Pending (Possible Point(s): 0)
| Average score |
|
| Your score |
|
Categories
- Not categorized 0%
-

Daww you didn’t pass. Keep trying. You need to score at least 65% to pass.
-

Good! You scored above 65%. You have won a bronze medal. This earns you 1 braindollar! Go for gold?
-

Very good! You scored above 80%. You have won a silver medal. This earns you 10 braindollars! Go for gold?
-

Congrats! You scored above 90%! You have won a gold medal. This earns you 100 braindollars!
| Pos. | Name | Entered on | Points | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Table is loading | ||||
| No data available | ||||
- 1
- 2
- Current
- Review
- Answered
- Correct
- Incorrect
-
Question 1 of 2
1. Question
.
-
A graph of the successive ionization energies of an element is shown below.
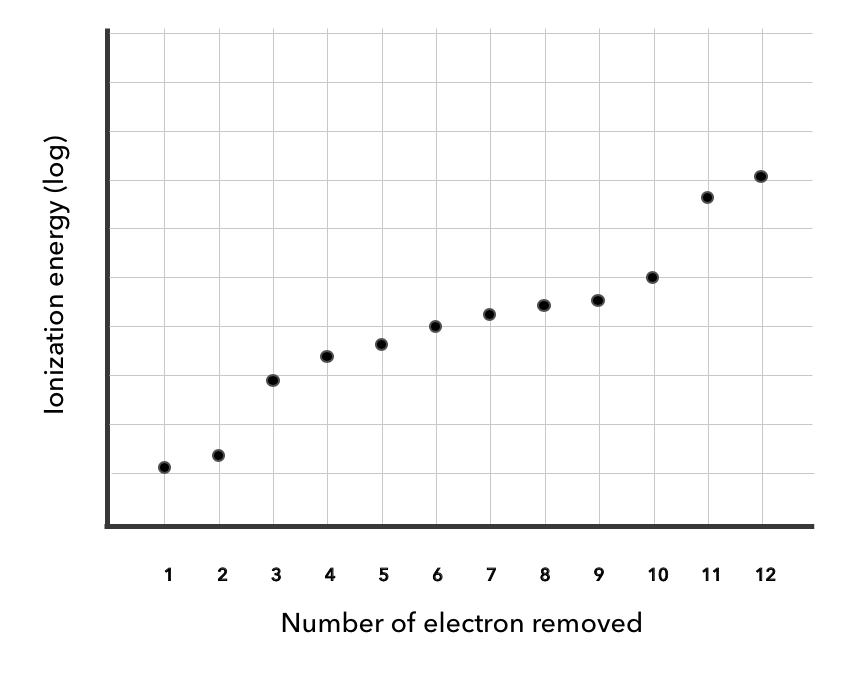
a. Deduce the group of the element.(1)
The element is in group
b. Explain the sharp increase in ionization energy between the 2nd and 3rd electrons. (2)
- Since the 3rd electron is in a lower shell, it is much to the nucleus than the 2nd electron.
- The 3rd electron is relatively shielded. So it is exposed to a greater effective charge.
c. Explain the rise in ionization energies from the 3rd to the 10th electrons. (1)
- As successive electrons are removed, reduced electron-electron brings electrons closer to the , such that they require energy to remove.
Fill in ALL blanks above with the following options:
[ less || more || 1 || 12 || 13 || 14 || closer || nuclear || nucleus || electron || repulsion || attraction ]
Correct 7 / 7 PointsIncorrect / 7 Points -
-
Question 2 of 2
2. Question
.
-
A graph of the first ionization energies of period 3 elements is shown below
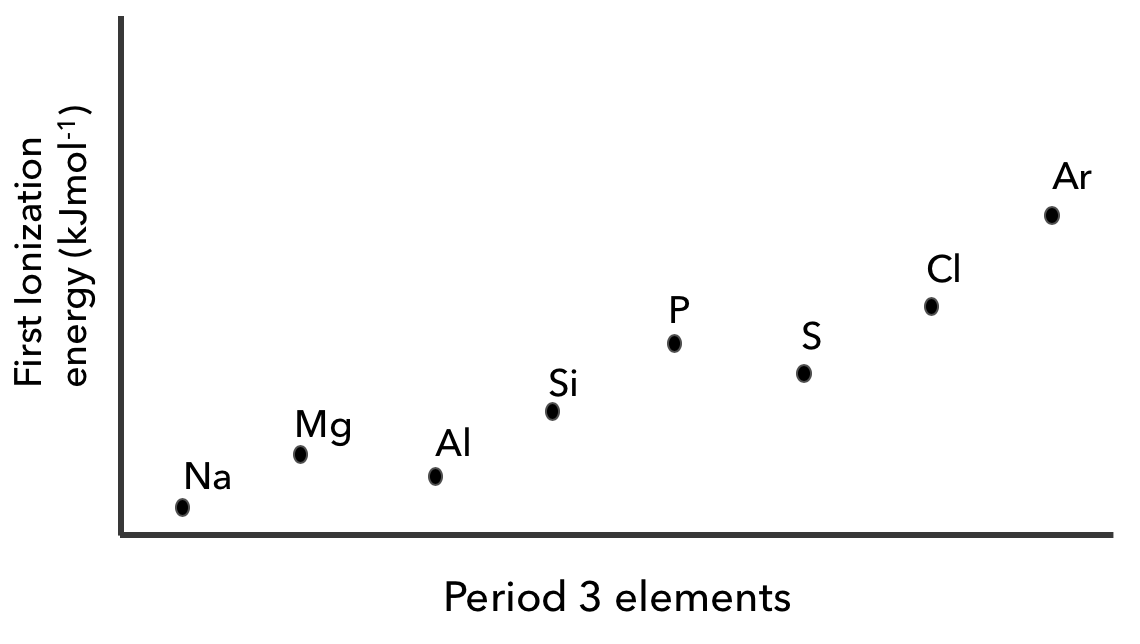
a. Explain why the first ionization energy is higher for magnesium than it is for sodium. (1)
- Magnesium has a nuclear charge than sodium. This attracts electrons more strongly, making them harder to remove.
b. Explain why the first ionization energy is lower for aluminium than it is for magnesium (1)
- The most loosely held electron in aluminium is in a orbital, but for magnesium, it is in a orbital. The orbital is higher energy and easier to remove.
c. Explain why the first ionization energy is lower for sulfur than it is for phosphorus. (1)
- Sulfur contains one 3p orbital, while phosphorus only has singly-occupied orbitals. The electron-electron in the paired orbital makes it easier to remove one of the electrons.
Fill in ALL blanks above with the following options:
[ lesser || greater || 3d || 3s || 3p || 4s || 4p || unpaired || paired ]
Correct 8 / 8 PointsIncorrect / 8 Points -
